“ Society 5.0 dan Industry 4.0 ” : Platform dan Akseleran Provinsi Jawa Timur menjadi Lumbung Biogas Nasional ?
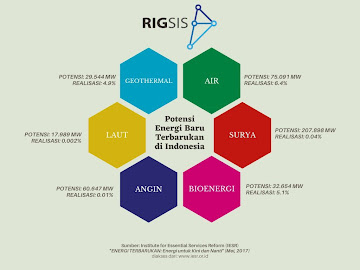
Indonesia memiliki potensi energi terbarukan yang besar, mencapai 400 GW. Dan sangat penting untuk mengatur sistem pemanfaatan energi dengan melakukan langkah-langkah strategis dalam mengatur (pemanfaatan) energi ini Arifin Tasrif, Menteri Energi dan Sumber Daya Mineral Indonesia Suatu pernyataan yang manis perihal energi terbarukan oleh Bapak Menteri, orang yang selalu disibukkan akan dinamisasi tata kelola pemanfaatan keenergian di negeri ini, khususnya energi terbarukan. Hanya dengan menukil satu induk kata dari berbagai varian energi terbarukan, yakni “bio-energy”, terlahirlah semangat melakukan eksploitasi dan manajemen potensinya yang menghasilkan berbagai jenis bentuk energi, seperti biofuel, biogas, dan biomassa. Pantaslah pelabelan " Lumbung Bioenergi Dunia" segera negeri ini dapatkan mengingat potensi bioenergi yang dapat dihasilkan menduduki peringkat 4 terbesar di Indonesia yakni sebesar 32.6 GW. Sangat menarik jika pendalaman parsial terkait pengaturan pe...
